With the continuous development of China’s society and economy, people’s aspirations for a better life continue to rise, and high-quality water supply has become an important part of this better life. Guided by the new national standard “Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water” (GB 5749-2022), Lihe Technology, under the guidance of the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed an online early warning system based on the detection of odor-producing genes in algae and other related products for source water odor issues, ensuring the safety of drinking water quality.
Odor-Producing Algae Early Warning System
In summer, earthy and musty odors frequently occur in reservoir water sources. 2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) and geosmin (GSM) are two typical earthy and musty odor compounds newly included in the revised “Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water” (GB 5749-2022). These odor compounds mainly originate from secondary metabolites of cyanobacteria, and their causes are complex. Currently, there is no mature early warning method for these odors, leading to passive and delayed responses by water treatment plants. The research group led by Professor Yang Min at the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, discovered that detecting odor-producing genes can predict the risk of odor-producing algae outbreaks one week in advance. Based on this discovery, Lihe Technology and the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences jointly developed the Odor-Producing Algae Early Warning System (GWD-1500). This equipment, the first of its kind in the world, automatically completes sample collection, pretreatment, injection, detection, and real-time analysis of results, providing water treatment plants with sufficient time to take targeted measures and achieving early detection, early warning, and early treatment of odor risks.
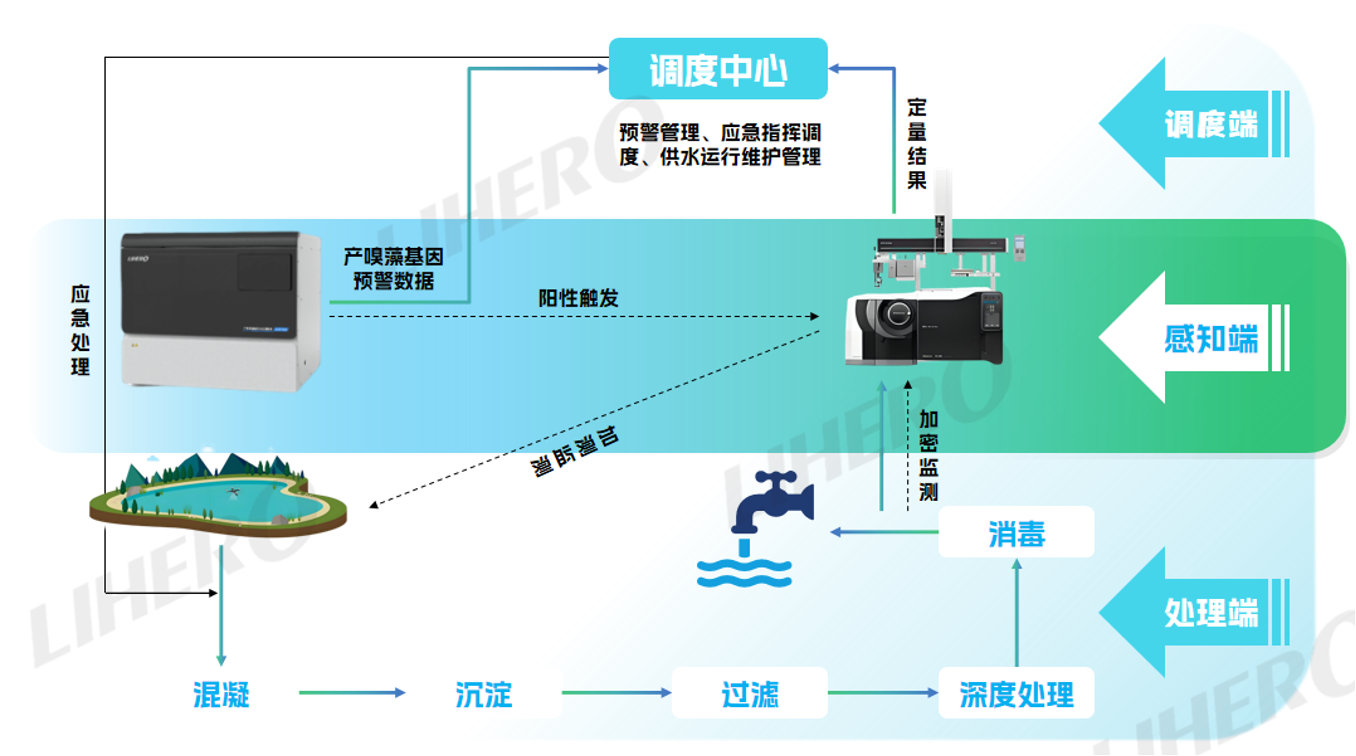
At the same time, leveraging its strengths in equipment development, Lihe Technology has also developed an online odor compound monitoring system based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technology. This system can detect approximately 100 common odor-causing compounds, including MIB, geosmin, dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), and dimethyl trisulfide (DMTS).

This system features full-process automation, 24-hour unmanned operation, real-time upload of early warning monitoring data, reliable results, long maintenance cycles, and high cost-effectiveness. It achieves a closed-loop management from “prevention before occurrence” to “precise intervention,” combining the triple advantages of “speed, accuracy, and economy.”
Performance Parameters
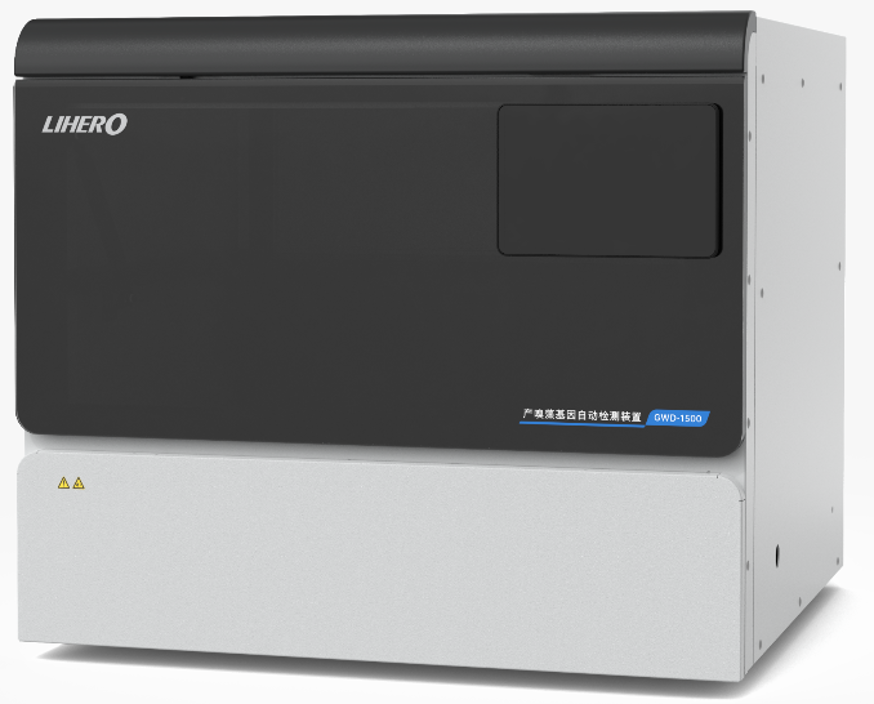
GWD-1500 Automatic Odor-Producing Gene Detection Device
-
Detection Limit: Can detect gene concentrations ≤10 copies/mL
-
Repeatability: Ct value variation ≤ ±0.5
-
Throughput: Each membrane module can perform 15 consecutive enrichment and detection cycles
- Warning Parameters: Geosmin, 2-methylisoborneol (expandable to other odor compounds)

LIHREO GMS 9100 Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer
-
Detection Limit:
- 2-Methylisoborneol and geosmin: ≤3 ng/L
- Dimethyl disulfide and dimethyl trisulfide: ≤10 ng/L
- 2-Methylisoborneol and geosmin: ≤3 ng/L
-
Repeatability: ≤10%
-
Maximum Scan Rate: 20,000 amu/s
- Odor Database: Approximately 100 odor compounds

Product Advantages
Combination of Early Warning and Precise Detection: Builds a full-cycle defense line of “warning-confirmation-response.” The GWD-1500 Odor-Producing Algae Gene Automatic Monitoring Device issues warnings 7–15 days before the production of odor compounds during the early stages of algal proliferation. After warning, it automatically activates the LIHREO GMS9100 Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer for detection, allowing adjustment of process parameters and chemical dosing based on the results, reducing operational costs for water treatment plants.
Full-Process Automation: Both the GWD-1500 Odor-Producing Algae Gene Automatic Monitoring Device and the LIHREO GMS9100 Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer can operate fully automatically.
24-Hour Unmanned Operation: The instruments operate automatically, with maintenance cycles ≥15 days under normal conditions, achieving 24-hour unmanned operation.
Accurate and Reliable: Meets the requirements of the “Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water” (GB 5749-2022).
Customizable and Expandable Parameters: Can be customized to expand other odor compounds produced by algae, such as sulfur ethers and aldehydes.
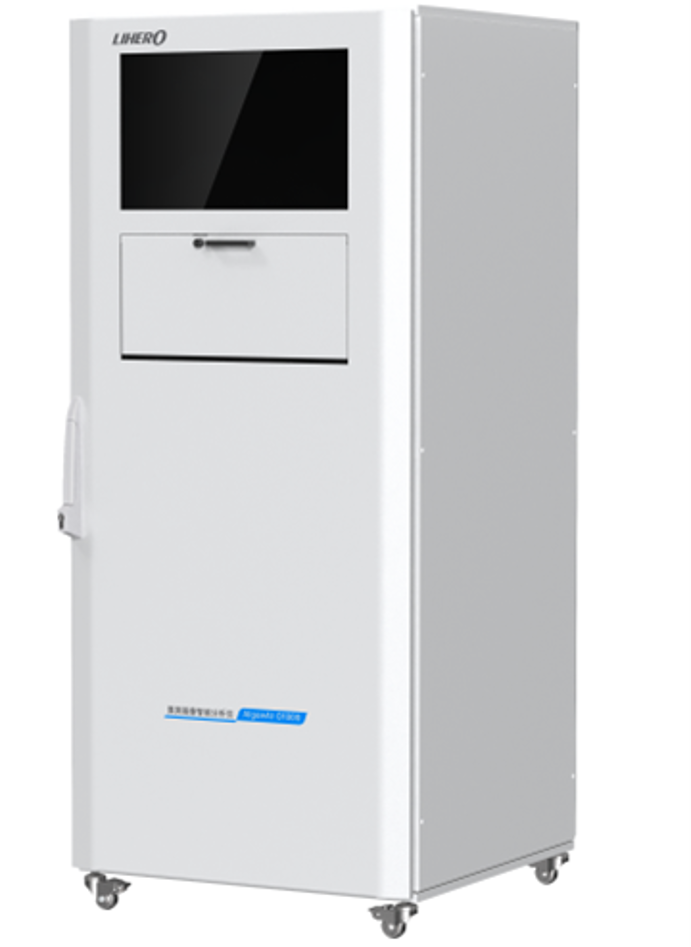
AlgaeAI-O1000 Online Algae Intelligent Analyzer
To achieve precise monitoring and early warning of algal blooms and help address the frequent occurrence of water blooms nationwide, Lihe Technology has independently developed portable algae analyzers and algae image intelligent analyzers. These are widely used for online monitoring and early warning of algae in rivers, lakes (reservoirs), and other water bodies, as well as in water treatment plants and aquaculture, providing data support for algae removal process adjustments in water treatment plants and targeted algae management in aquaculture.

Instrument Introduction
The Online Algae Intelligent Analyzer is designed and developed in accordance with the “Water Quality—Determination of Phytoplankton—Microscopic Counting Method with 0.1 ml Counting Frame” (HJ 1216-2021). It constructs an AI recognition model for algae based on deep learning technology combined with an expert knowledge base. Through automatic sampling technology and fully automated microscopic imaging technology, it provides detailed information on algal genera, density, dominance, and diversity in water bodies, achieving automation, intelligence, and de-professionalization of algal genus analysis. Compared to traditional manual methods, the Algae Intelligent Image Recognition System achieves an accuracy of 90% and a counting precision of ≤15%. Additionally, it offers the following advantages.
Key Features
Automated Process: Automatic pretreatment technology enables online operation without manual intervention.
Fast Analysis: Completes the full process (100 fields of view) for one sample in 30 minutes.
Deep Neural Network Technology: Features more hidden layers, enabling the processing of more complex and abstract characteristics.
Expert Database: Includes over 100 algal genera from multiple watersheds, providing broad recognition coverage. It can also expand local algae databases based on instrument operation data and the characteristics of local water bodies.